Morse Code Converter
Introduction
Morse code is a method of encoding text characters using sequences of dots and dashes (or short
and long signals). Each letter of the alphabet, along with numbers and some special characters,
is represented by a unique pattern of short signals (dots) and long signals (dashes).
Developed in the early 1830s by Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail, Morse Code was originally designed
for telegraphy, but its influence has transcended time and technology.
Principle
The principle behind Morse code is based on the use of combinations of dots (.) and dashes (-) to represent letters, numbers, and punctuation marks. Each character in Morse code is assigned a unique sequence of these signals, allowing messages to be transmitted efficiently using telegraphy, radio signals, or light flashes. This principle of encoding information through a binary system of short and long signals forms the foundation of Morse code communication.
Morse Code Table
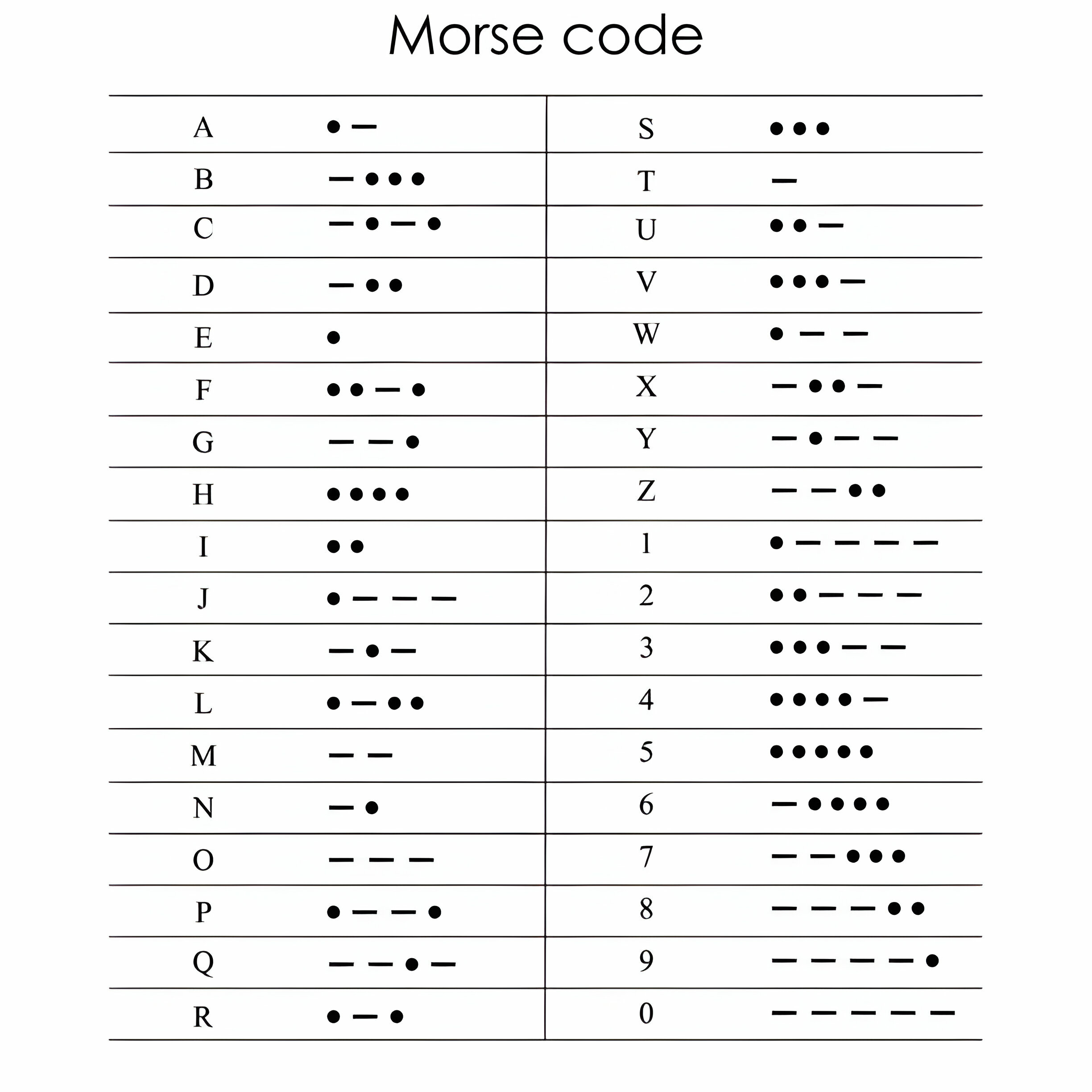
Applications
Morse code has several applications. Some of them are:
• Morse Code is used in telecommunications, especially in situations where voice
communication is not possible or practical.
• It is used in aviation and nautical industries for sending distress signals,
traditionally known as an SOS signal.
• Amateur radio enthusiasts and ham radio operators often use Morse Code as a form of
basic communication.
• Morse Code has been used in assistive technology to provide communication capabilities
to people with disabilities, using a series of "dots" and "dashes" to represent letters and
numbers.
• It has also been used in military operations for secure and discreet communication.